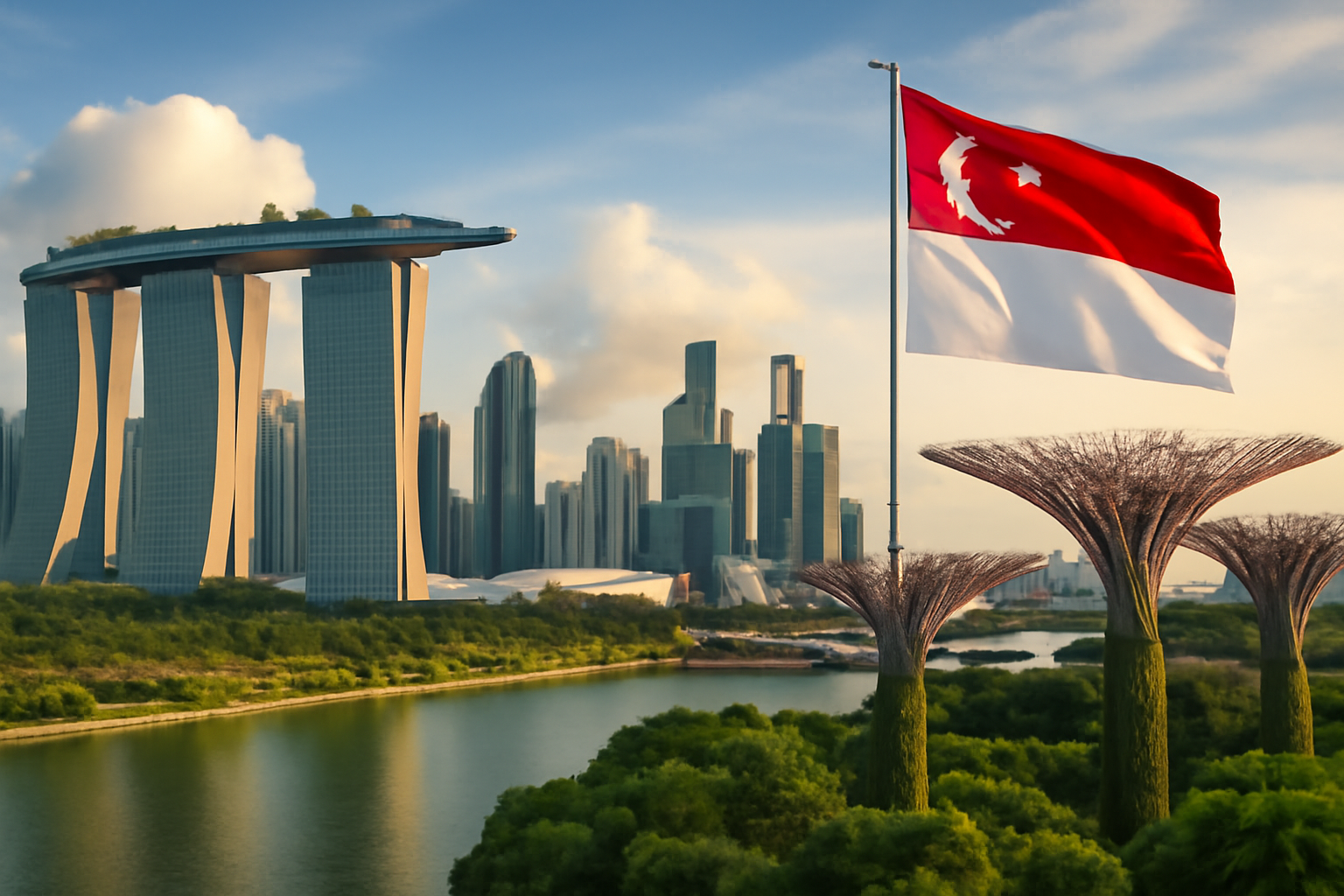
Singapore, an island city-state located at the crossroads of Asia, has carved out a reputation for itself on the global stage. Its transformation from a small British colonial port into one of the world’s most prosperous economies has sparked fascination and admiration across the globe. Today, Singapore is viewed as a global financial hub, a model of effective governance, and a symbol of what is possible through economic planning and social cohesion.
One of the key factors contributing to Singapore’s positive global perception is its economic success. As one of the wealthiest nations in the world in terms of GDP per capita, Singapore is seen as a powerhouse of business, finance, and trade. The country has developed a robust economy by strategically positioning itself as a global hub for industries such as finance, biotechnology, and technology. Its strong business environment, low taxes, and world-class infrastructure have made it an attractive destination for foreign investments and multinational corporations, further enhancing its global standing.
Singapore’s focus on sustainability and innovation has also garnered significant international attention. The city-state is known for its cutting-edge approach to urban planning, incorporating green spaces into its urban landscape and leading the charge in smart city development. The nation’s commitment to environmental sustainability, from its water management systems to its green building initiatives, has solidified its image as a forward-thinking and environmentally responsible country.
Additionally, Singapore’s political landscape plays a significant role in shaping its global image. With a stable, highly organized government led by the PAP, the city-state has maintained a reputation for political order and safety. This stability has been instrumental in fostering Singapore’s rapid economic growth, but it has also raised concerns about the lack of political freedoms and the dominance of the ruling party. While the government’s policies have been credited with creating a secure environment for citizens and businesses, some critics argue that the restrictions on freedom of speech and assembly limit democratic expression.
The country’s commitment to racial and religious harmony is another aspect that defines its global image. With a diverse population consisting of ethnic Chinese, Malays, Indians, and others, Singapore is seen as a model of multiculturalism. The government has implemented policies that promote social integration, creating an environment where different communities live and work together in relative peace. Globally, Singapore is recognized as a shining example of how diverse societies can coexist without succumbing to division or conflict.
On the international front, Singapore is known for its diplomatic efforts and active participation in global affairs. The city-state has earned a reputation for being a neutral and pragmatic player in international relations. Singapore is a key advocate for free trade and open markets, and it plays an important role in international organizations such as the United Nations, ASEAN, and the World Trade Organization. Its diplomatic neutrality allows it to maintain strong relationships with a wide range of countries, enhancing its global influence.
In essence, Singapore’s reputation on the world stage is a product of its unique combination of economic prosperity, political stability, multicultural harmony, and active global engagement. Despite its small size, Singapore has emerged as a powerful player on the international scene, with a global image that continues to evolve and grow as the city-state continues to innovate and expand its global reach.