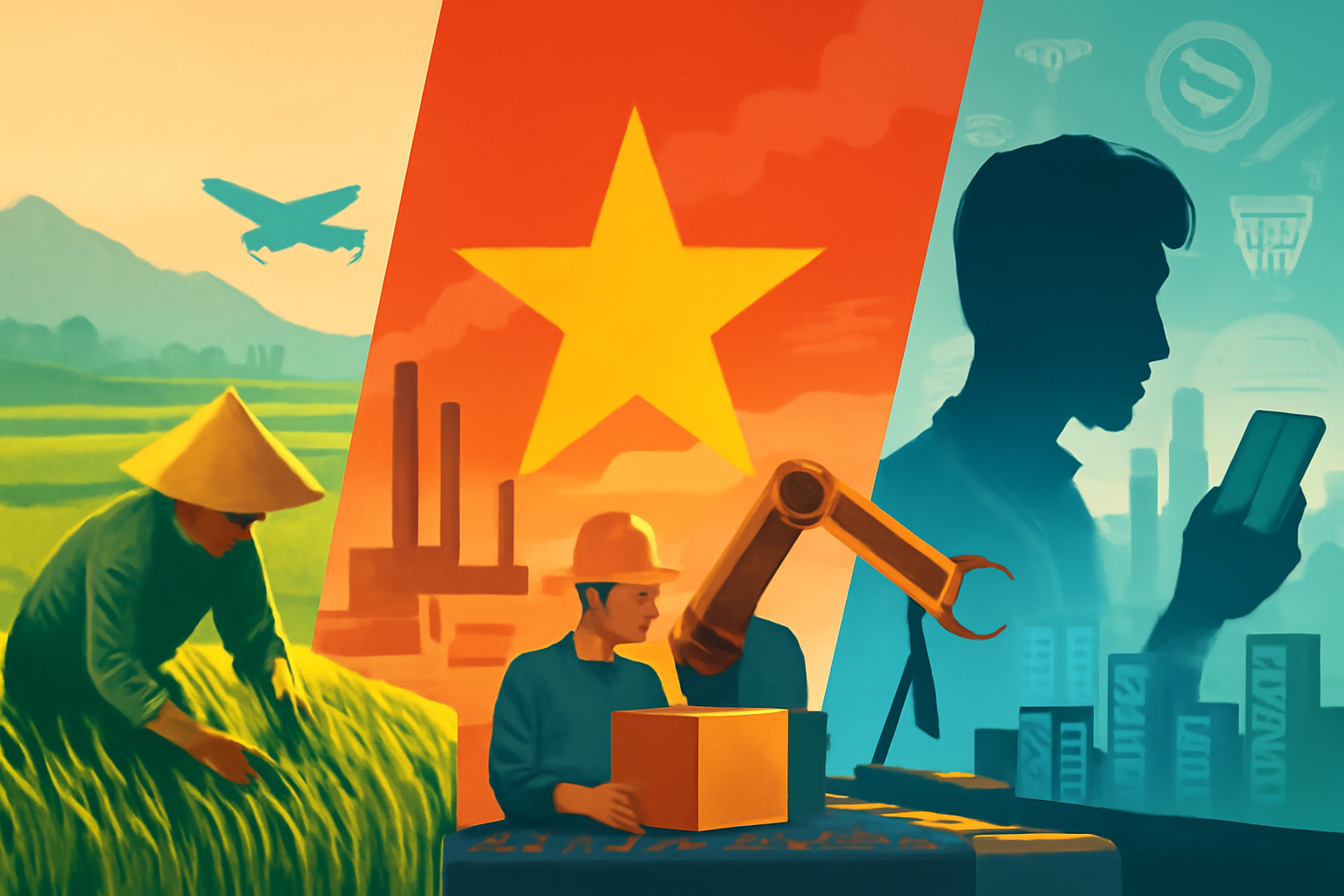
Vietnam, a country once dependent on its agricultural base, has undergone a profound economic transformation. Today, it stands as a testament to the power of strategic planning and reform, transitioning from an agrarian society to an industrial and technological powerhouse. This shift has been driven by both internal changes and its growing engagement with the global economy.
Agriculture: The Pillar of Vietnam’s Early Economy
For much of its history, Vietnam’s economy relied heavily on agriculture, with rice being the cornerstone of both domestic consumption and export. Agriculture was the primary source of livelihood for the population, and the country’s agricultural exports played a significant role in its trade relations, especially in the global rice market. However, as the world economy began to change in the late 20th century, the Vietnamese government recognized the limitations of an economy based solely on agriculture.
The government initiated reforms in the 1980s that opened up markets and improved agricultural practices. Vietnam’s rice production became more efficient through the introduction of modern farming techniques and better irrigation systems. This allowed the country to not only feed its population but also to increase its agricultural exports, positioning Vietnam as one of the largest exporters of rice globally.
Industrialization: A New Economic Era
The 1990s marked a pivotal moment in Vietnam’s economic journey as the country embraced industrialization. Foreign direct investment (FDI) began pouring in, especially in the manufacturing sector. Industrial zones and free trade agreements became the backbone of this transformation, drawing international companies looking for low-cost, efficient manufacturing hubs. The establishment of these zones facilitated the growth of key industries such as electronics, textiles, and automotive manufacturing.
The shift toward industrial production brought about rapid urbanization and job creation, transforming the economy from one based on subsistence farming to a more diversified, export-driven industrial powerhouse. As Vietnam became increasingly integrated into global supply chains, it began to export a wide range of manufactured goods, including electronics, clothing, and footwear, with key players like Samsung setting up large-scale operations in the country.
Technological Innovation: Shaping Vietnam’s Digital Future
Vietnam has also embraced the digital revolution, positioning itself as a leading player in Southeast Asia’s technology sector. The government has made significant strides in creating a supportive environment for tech startups and digital enterprises, fostering innovation in areas such as software development, e-commerce, and fintech.
The rapid rise of local companies such as Zalo, a popular messaging app, and MoMo, a leading digital wallet platform, reflects the growing importance of technology in Vietnam’s economy. The Vietnamese government’s support for innovation and its focus on improving digital infrastructure have played a key role in these successes. Additionally, Vietnam has invested heavily in enhancing its digital infrastructure, with the government working to expand internet access and improve the country’s digital literacy rates.
Vietnam’s young, tech-savvy population has also contributed to the rapid expansion of its digital economy. With one of the highest internet penetration rates in the region, the country is seeing a surge in e-commerce and digital services. This tech-savvy population is driving demand for new digital products and services, further boosting the country’s economic growth.
Vietnam’s Future: Continued Growth and Challenges
As Vietnam continues its journey toward a fully industrialized and tech-driven economy, challenges remain. The country must overcome issues such as income inequality, environmental concerns, and the need for a skilled workforce. Additionally, Vietnam’s infrastructure must keep pace with its rapid industrialization to sustain growth.
Nevertheless, with its robust industrial base and a thriving technology sector, Vietnam’s economic future looks promising. The country’s successful transition from agriculture to industry and technology underscores its adaptability and potential to become a key global player in the years to come.