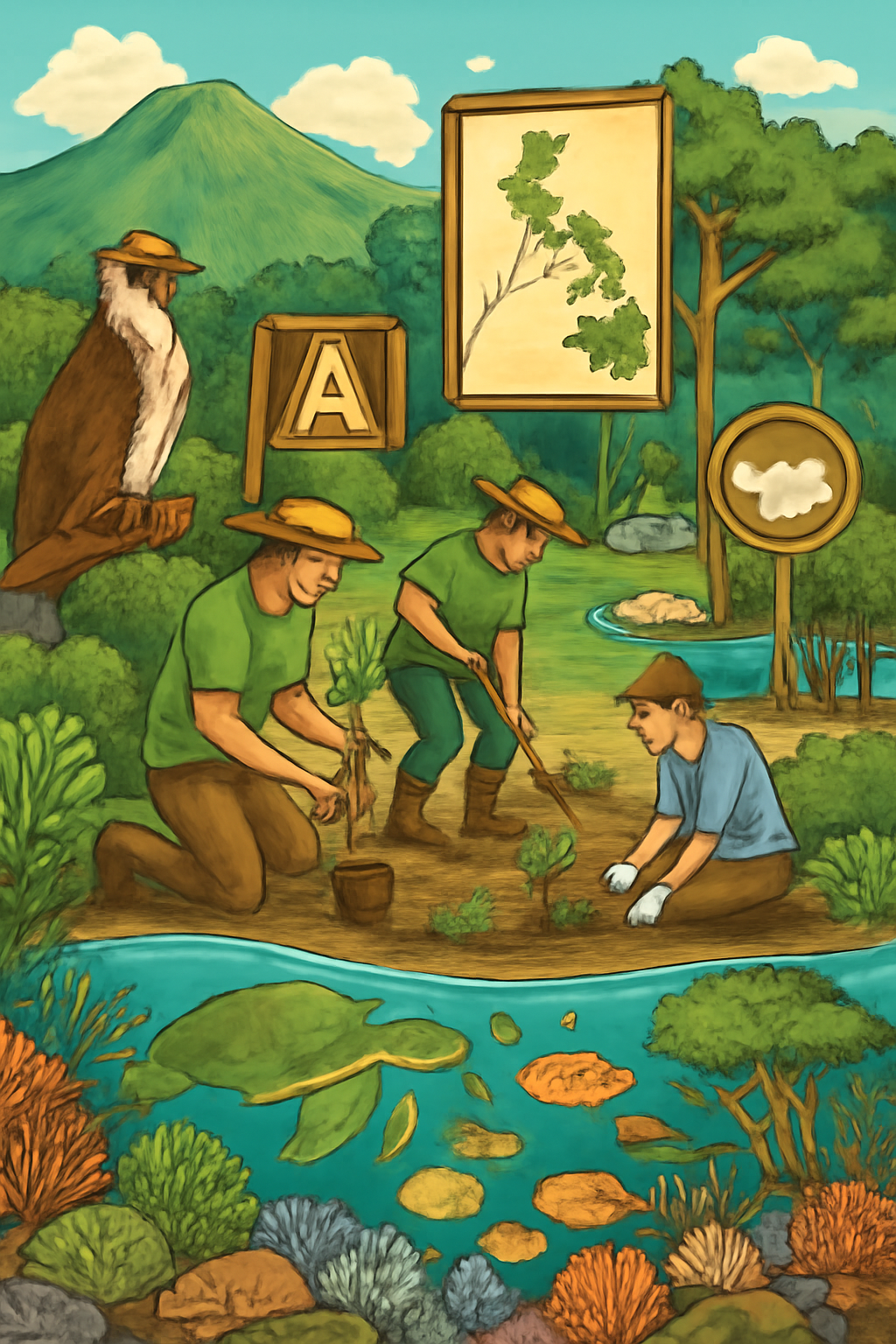
The Philippines is home to an extraordinary variety of ecosystems, ranging from lush tropical rainforests to vibrant coral reefs. With its rich biodiversity, it’s often referred to as one of the world’s “megadiverse” countries. However, the pressures of industrial development, population growth, and climate change have put these precious ecosystems at risk. In recent years, the Philippines has taken significant steps to implement conservation strategies aimed at safeguarding its natural resources.
One of the foremost strategies is the establishment of protected areas across the country. The National Integrated Protected Areas System (NIPAS) Law, enacted in 1992, has paved the way for the creation of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and marine protected areas. These protected spaces are crucial for preserving the habitats of numerous endangered species such as the Philippine eagle and the Visayan warty pig, both of which are at the brink of extinction.
The Philippines has also embraced the concept of sustainable development. Many initiatives focus on balancing economic growth with environmental protection. In the forestry sector, the government introduced the National Greening Program (NGP) to restore degraded lands and improve forest cover. Through this program, thousands of hectares of land have been rehabilitated, helping to combat soil erosion and enhance water quality in the country’s rivers and lakes.
Marine conservation is another significant focus in the Philippines. Home to the Coral Triangle, the world’s center of marine biodiversity, the country has prioritized the protection of its coral reefs. Various local and international conservation groups are working in partnership with the government to create marine protected areas (MPAs) that restrict harmful fishing practices and promote sustainable fisheries management. Moreover, the country has launched a series of campaigns to raise awareness of the importance of marine ecosystems for both the environment and the local economy.
However, conservation efforts face multiple challenges, including illegal logging, mining, and overfishing. The government has enacted stricter regulations and imposed heavier penalties for environmental violations. Additionally, local communities play a vital role in conservation through participatory governance models that involve them in decision-making processes related to natural resource management.
Despite these challenges, the Philippines remains committed to preserving its natural heritage. The country’s efforts in environmental conservation are supported by both local and international organizations, underscoring the global importance of safeguarding biodiversity and ensuring a sustainable future for the archipelago.


![[Himala ng Niyebe at Cherry Blossoms] Isang natatanging karanasan sa taas na 1,900m: Maranasan ang “Snow Walls” at “Spring Snow Play” sa Otari Village, Nagano. May espesyal na operasyon sa maagang tagsibol hanggang Mayo 6; magbubukas ang Tsugaike Nature Park sa Hunyo 6.](https://asianicinsights.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/03/codeimg-233.jpg)